功能
gRPC是Google公司开源的一个远程服务调用框架,基于HTTP2协议。
特点
- 通过接口定义语言(IDL)定义了客户端与服务端数据交换的格式,该文件的扩展名为
.proto, 通过将文件编译到对应的开发语言来完成系统的集成。
- gRPC使用高效的序列化工具
Protocol buffer
在SpringBoot中使用gRPC完成服务间调用
完整的代码地址
方法及参数对象声明
首先我们需要声明服务调用的接口方法与参数,推荐使用proto3,通过在pom中使用protobuf-maven-plugin插件,可以在编译的时候将.proto文件生成java class文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| syntax = "proto3";
option java_multiple_files = true;
package com.vcors.demo.grpcproto;
message Person {
string first_name = 1;
string last_name = 2;
}
message Greeting {
string message = 1;
}
service HelloWorldService {
rpc sayHello (Person) returns (Greeting);
}
|
服务端开发
理解.proto代码生成
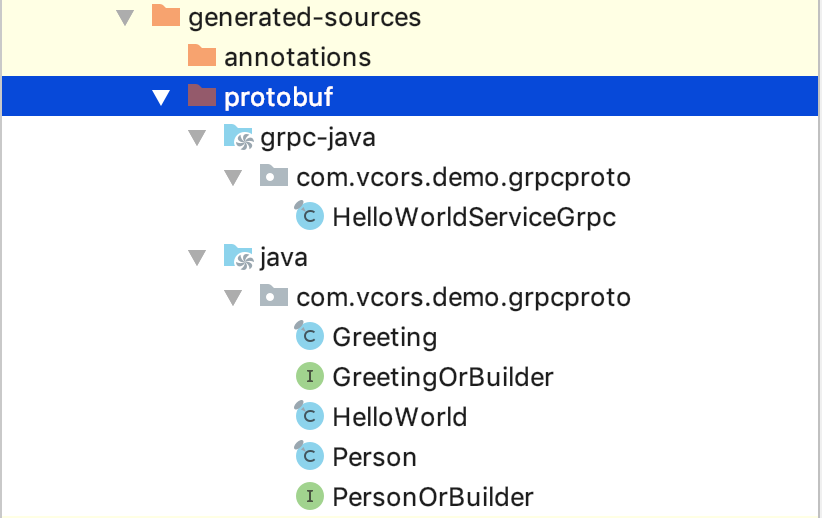
- 对于
.proto文件中定义的对象,会生成对应的JavaClass,这是可以通过Protocal Buffers序列化的对象模型
- 对于
.proto文件中定义的方法,会生成XXXGrpc
XXXGrpc
接口方法声明
1
| public static abstract class HelloWorldServiceImplBase implements io.grpc.BindableService {}
|
这个抽象内部类主要用来集成在服务端,作为方法实现的父级接口
方法存根
种类分为
集成依赖
在服务端中集成proto模块声明的模型和接口方法
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.vcors.demo</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-proto</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
|
方法实现
通过继承HelloWorldServiceGrpc.HelloWorldServiceImplBase来重写.proto接口中声明的方法,也就是具体业务需要实现的逻辑代码都在这
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| @GRpcService
public class HelloWorldServiceImpl extends HelloWorldServiceGrpc.HelloWorldServiceImplBase {
private static final Logger LOGGER =
LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldServiceImpl.class);
@Override
public void sayHello(Person request, StreamObserver<Greeting> responseObserver) {
LOGGER.info("server received {}", request);
String message = "Hello " + request.getFirstName() + " "
+ request.getLastName() + "!";
Greeting greeting =
Greeting.newBuilder().setMessage(message).build();
LOGGER.info("server responded {}", greeting);
responseObserver.onNext(greeting);
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
|
客户端调用服务端
创建存根接口
首先在客户端中也同样要在pom中集成proto声明模块
创建存根方法对象
1
2
3
4
| ManagedChannel managedChannel = ManagedChannelBuilder
.forAddress("localhost", 6565).usePlaintext().build();
helloWorldServiceBlockingStub =
HelloWorldServiceGrpc.newBlockingStub(managedChannel);
|
执行方法调用
像调用本地方法一样,实现不同应用接口的调用
1
2
| Greeting greeting =
helloWorldServiceBlockingStub.sayHello(person);
|
测试
同时启动服务端与客户端应用,调用客户端接口来收到服务端的正确响应
理解gRPC-spring-boot-starter
gRPC-spring-boot-starter 是对GRpcServer的一个封装,可以使我们在spring-boot项目中更简单的使用GRpc,核心功能就是启动了GRpcServer,并将通过@GRpcServer注解的Service注册到Server中
理解GRpcAutoConfiguration
在grpc-spring-boot-starter/META-INF/spring.factories配置了GRpcAutoConfiguration, springboot启动时会自动加载该配置文件
该文件主要初始化了以下几个Bean实例
- GRpcServerRunner
- HealthStatusManager
- GRpcServerBuilderConfigurer
理解GRpcServerRunner
启动一个GRpc Server, 集成到SpringBoot中后,项目无需再集成其他的web server
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
log.info("Starting gRPC Server ...");
Collection<ServerInterceptor> globalInterceptors = (Collection)this.getBeanNamesByTypeWithAnnotation(GRpcGlobalInterceptor.class, ServerInterceptor.class).map((name) -> {
return (ServerInterceptor)this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getBean(name, ServerInterceptor.class);
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
this.serverBuilder.addService(this.healthStatusManager.getHealthService());
this.getBeanNamesByTypeWithAnnotation(GRpcService.class, BindableService.class).forEach((name) -> {
BindableService srv = (BindableService)this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getBean(name, BindableService.class);
ServerServiceDefinition serviceDefinition = srv.bindService();
GRpcService gRpcServiceAnn = (GRpcService)this.applicationContext.findAnnotationOnBean(name, GRpcService.class);
serviceDefinition = this.bindInterceptors(serviceDefinition, gRpcServiceAnn, globalInterceptors);
this.serverBuilder.addService(serviceDefinition);
String serviceName = serviceDefinition.getServiceDescriptor().getName();
this.healthStatusManager.setStatus(serviceName, ServingStatus.SERVING);
log.info("'{}' service has been registered.", srv.getClass().getName());
});
if (this.gRpcServerProperties.isEnableReflection()) {
this.serverBuilder.addService(ProtoReflectionService.newInstance());
log.info("'{}' service has been registered.", ProtoReflectionService.class.getName());
}
this.configurer.configure(this.serverBuilder);
this.server = this.serverBuilder.build().start();
this.applicationContext.publishEvent(new GRpcServerInitializedEvent(this.server));
log.info("gRPC Server started, listening on port {}.", this.server.getPort());
this.startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
|
理解@GRpcService
通过该注解声明的方法会被声明为Spring Bean,本质上它是一个@Service注解,另外就是在启动GRpcServer时会注册该Bean。
Next
- 接口调用的认证处理
- 结合Kubernetes平台实现服务发现与负载均衡






